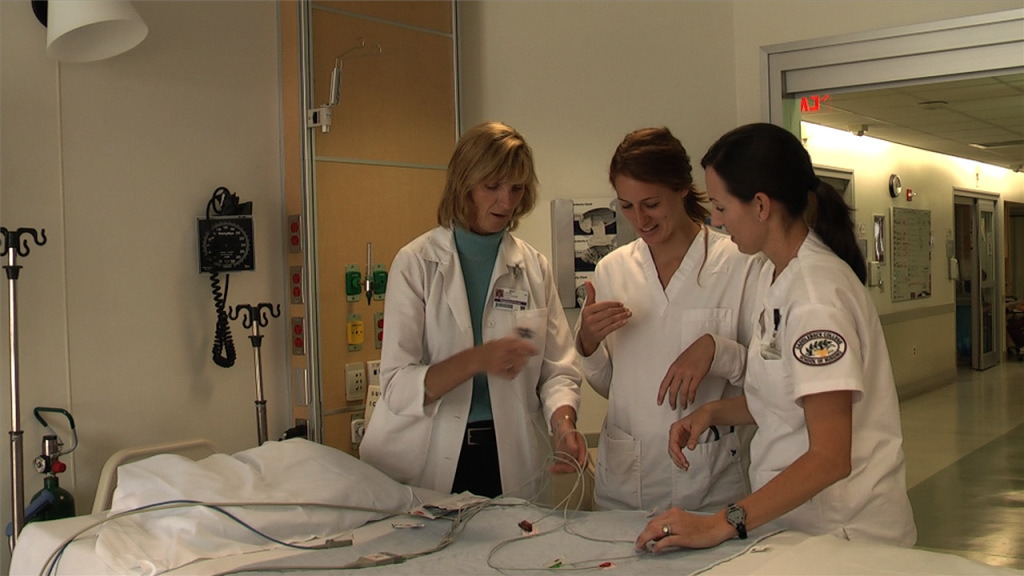
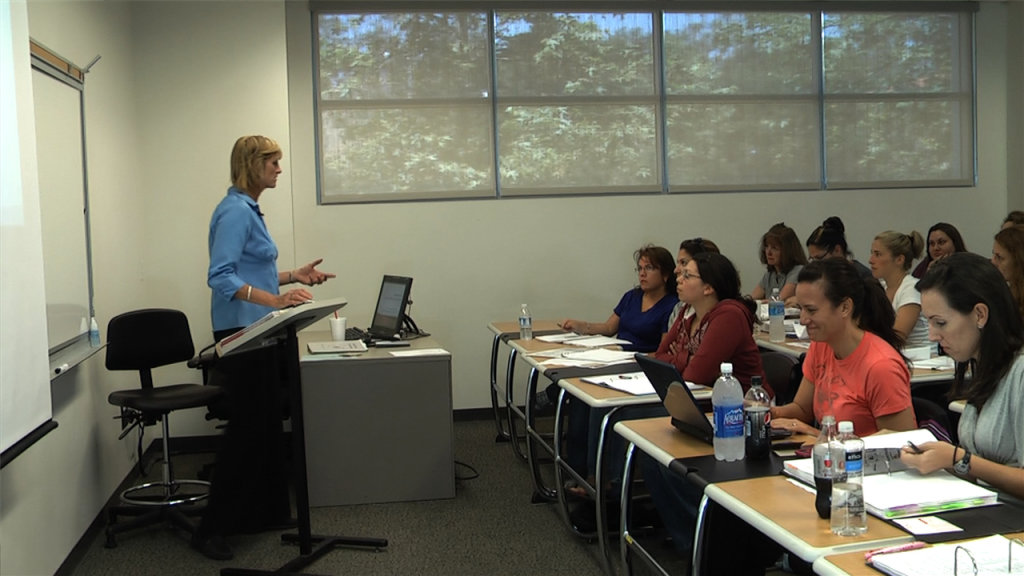
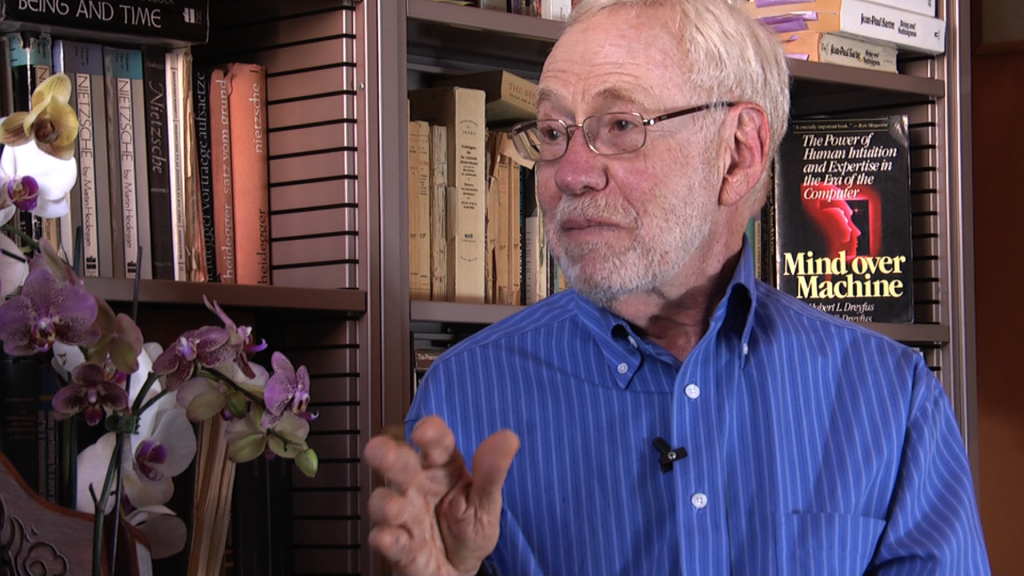
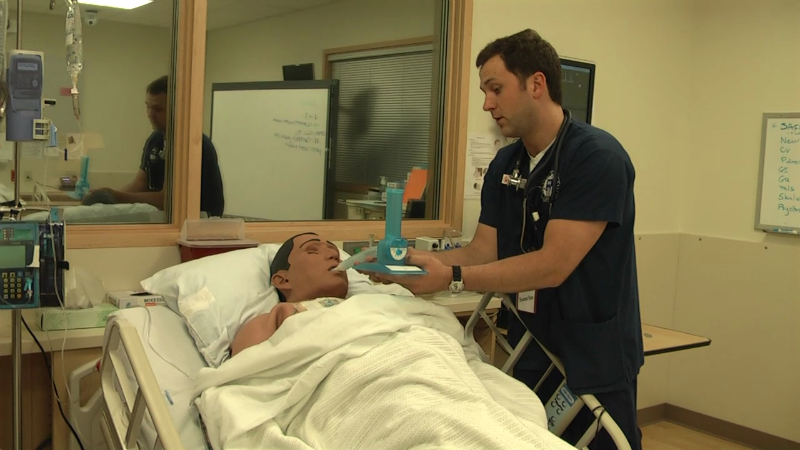
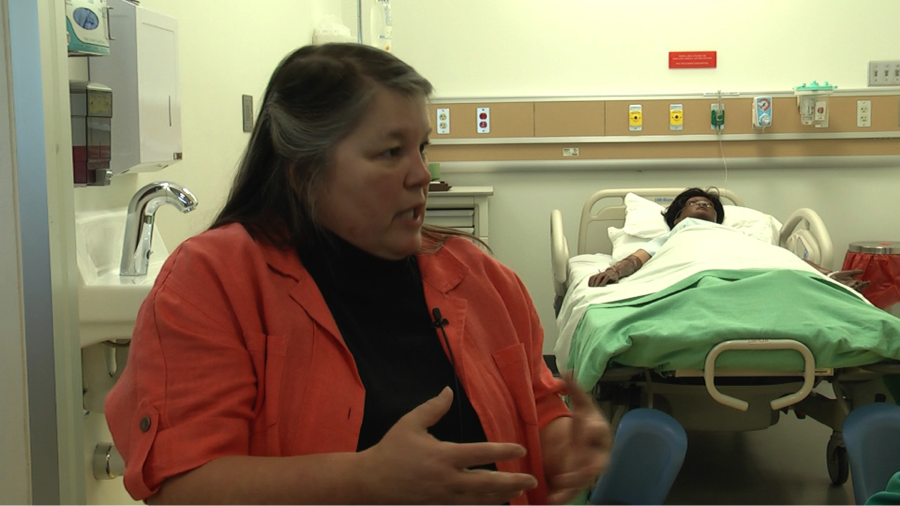
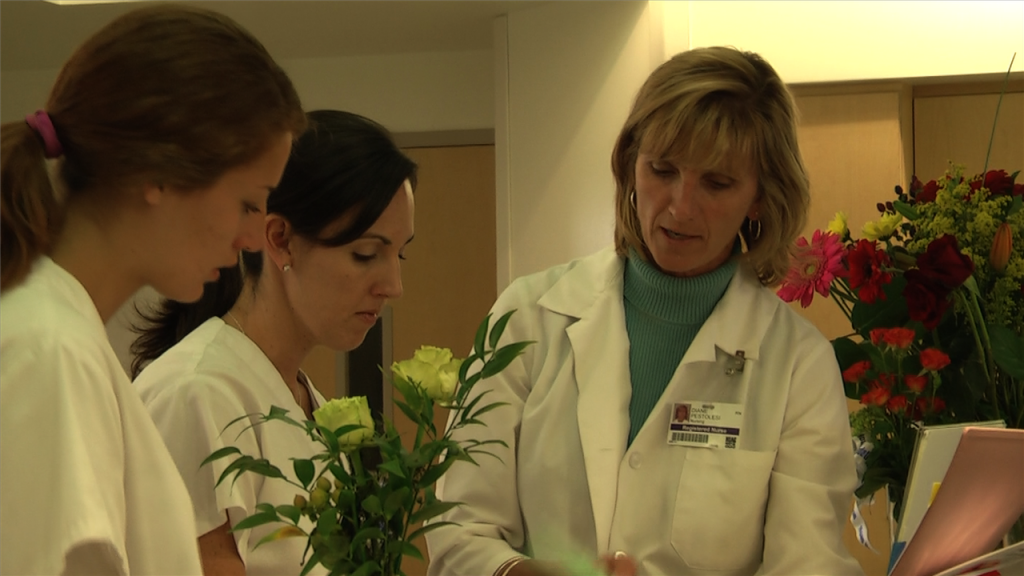
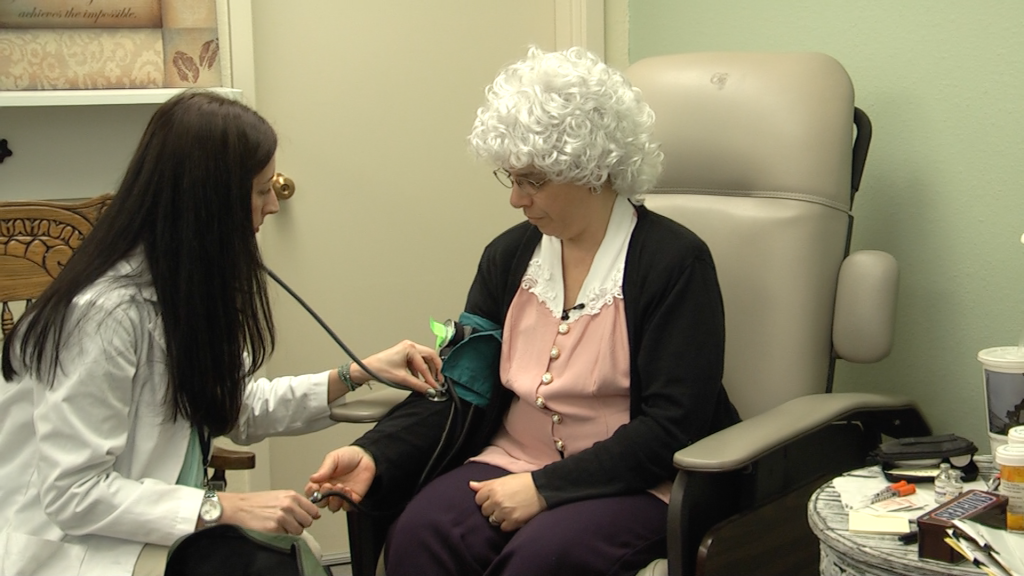
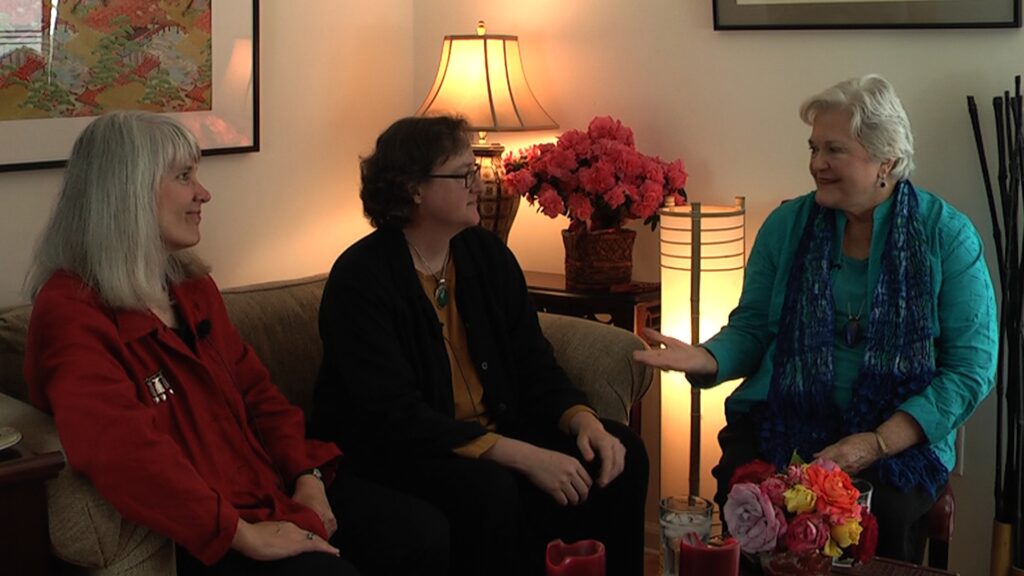VIDEO: Experiential Learning in Sim Classes PT. 1
Patricia Benner, MSN, R.N. Ph.D., FAAN. How Simulation learning meets the challenge of limited clinical placements. How integrating Sim with all…
VIDEO: Experiential Learning in Sim Classes PT. 1

VIDEO: Experiential Learning in Sim Classes PT. 2
Patricia Benner, MSN, R.N. Ph.D., FAAN. How Simulation learning meets the challenge of limited clinical placements. How integrating Sim with all…
VIDEO: Experiential Learning in Sim Classes PT. 2

VIDEO: Crafting Simulation Clinical Learning
Patricia Benner, MSN, R.N. Ph.D., FAAN. Three key faculty innovators describe how this Sim program prepares students to be more practice-ready.…
VIDEO: Crafting Simulation Clinical Learning

VIDEO: Impact on Students — The Difference this Sim Program has made on Students
Patricia Benner, MSN, R.N. Ph.D., FAAN. Three freshmen nursing students describe the profound impact this Sim experience has had on their…
VIDEO: Impact on Students — The Difference this Sim Program has made on Students
Get Started with EducatingNurses.Com
How to Create Your Account
Focus Area 1
Educating Nurses: A Call for Radical Transformation
This module was designed for new teachers, and those who want to make their teaching more interactive.
Anxiety and fear are two of the greatest learning impediments, yet student nurses and physicians and other professionals learn much of their profession in high risk clinical learning environments. Both the patients and students need clinical faculty willing to be their safety net. We teach in high fidelity simulations and in actual clinical assignments …
I hope that members will seriously consider the three positions for teachers and students in their stances: 1. Student Focused: A student centered stance, which focuses primarily, on the students’ preferences, choices, and concerns. 2. Teacher Focused: A teacher performance centered stance where the class, climate, culture and performance is focused on the teacher’s actions …
Continue reading “Moving to patient-focused, practice-focused teaching”
Focus Area 2
Preparing for Teaching and Learning for the Next Gen NCLEX-RN Exam and The 2021 AACN Essentials Document
This module was designed to help students uncover blind spots, and biases.
Why authentic, unfolding case studies are essential in the education of a nurse -Patricia Benner (copyright, 2011) Educational research supports the effectiveness of teaching students multiple ways of thinking, including clinical reasoning, critical thinking, and creative thinking. Clinical Reasoning is a form of practical reasoning, i.e., reasoning across time about the particular through changes in …
Continue reading “Teaching Our Students to Use Multiple Frames of Reference for Clinical Situations”
Copyright Patricia Benner Newsletter for February 2013 Teaching for a Professional Practice has many additional demands than an introductory survey course. In a professional practice we expect students to develop deep learning that includes the three professional apprenticeships common to Professional Education. Along with my Carnegie colleagues, I am using the word “apprenticeship” metaphorically, and …
Continue reading “Less is More: Thinking about Deep Learning”
Focus Area 3
Practice Readiness Through Enhancing Practice-Based Experiential Learning
This module can help the teacher recognize the challenges and strategies of working with Novice, Advanced Beginner, and Competent Nurses at their level of practice.
By: Patricia Benner We are learning more and more about the positive outcomes of engagement and the deleterious effects of disengagement (Rubin, 2009). In studies of skill acquisition and clinical reasoning we found that nurses who had problems with engaging with patients, families, and the actual demands, resources and challenges of particular situations did not …
Continue reading “Teaching and Learning Situated Skills of Involvement with Patients and Families”
By Patricia Benner, R.N., Ph.D. , Copyright 2015 Increasingly, clinical teaching is done by Clinical Adjunct Faculty, who may or may not have any formal education in teaching. Clinical Adjuncts may not have had much guidance about what the aims of particular clinical courses are or which students need situated coaching to address …
Focus Area 4
Experiential Learning
An effective, transformative curriculum needs to be coherent to the student and faculty engaging in the curriculum. This module can help the teacher design a Transformative Curriculum in Nursing Education
Patricia Benner, R.N., Ph.D., FAAN Learning a practice discipline is ideal for both simulation and direct experiential learning from practice. But the design of the simulations must be practice-domain specific and pedagogically sound for teaching good practice. Teaching nursing practice requires: -Experiential learning in high stakes environments -Expertise Depends on Relational Skills and Clinical Imagination …
Why authentic, unfolding case studies are essential in the education of a nurse -Patricia Benner (copyright, 2011) Educational research supports the effectiveness of teaching students multiple ways of thinking, including clinical reasoning, critical thinking, and creative thinking. Clinical Reasoning is a form of practical reasoning, i.e., reasoning across time about the particular through changes in …
Continue reading “Teaching Our Students to Use Multiple Frames of Reference for Clinical Situations”
Patricia Benner R.N., Ph.D., In Conversation and Association with Dr. Stephanie Sedaris, Copyright 2014 Most agree that much of the learning from simulation comes from post-simulation debriefing and reflection, yet faculty are in the earliest stages of conducting research or even describing what is most and least effective in debriefing sessions after simulations. Prior to …
Focus Area 5
Increasing Student Engagement and Interaction in Teaching and Learning
One of the oldest pedagogies is that of dialogue and questioning to prompt thinking and extending understanding of different sorts; I have the Socratic Dialogues in mind. Dr. Lee Shulman, former President of Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching speaks of “The Socratic Monologue” from his research on medical education. He describes a physician …
Continue reading “The Pedagogical Art of Asking Questions and Astute Listening”
Lectures should never be considered as a single intent, single style pedagogical strategy. By Patricia Benner, Copyright 2012 In this May Newsletter, we review some of the major legitimate pedagogical uses of lecture, in the classroom, seminar, skills lab. Pedagogical unsound uses of lectures (especially for nursing education) that should be avoided altogether are also …
As you put the final touches on your syllabi for the Fall Term, review your approach to the course with an eye to student engagement in learning. Instead of the limited behavioral objectives, you might add concrete practice-centered goals for the course. Do not be afraid of “I” statements…they can open communication between students and …
Continue reading “Creating An Engaging Adventuresome, Practice-Centered Syllabus”
Focus Area 6
Transforming Curriculum
This module explores strategies the teacher can use to engage their students in imagining relevant clinical situations.
by: Patricia Benner Many schools of nursing are embarked upon transforming their nursing curriculum in response to the Carnegie National Study of Nursing Education, the IOM/Robert Woods Johnson Futures Report, the Lancet Report, The Essentials of Baccalaureate Nursing Education, and the QSEN Report on Quality and Safety Education for Nurses. These external demands are met …
Continue reading “Designing a Transformative Curriculum in Nursing Education”
There are many pejorative terms to describe the conflicts, arguments and difficulties getting faculty “on the same page” or “going in the same direction.” Many call developing orchestrated activity on the part of diverse, creative, autonomy oriented, critical thinking faculty members like “herding cats.” But that is pejorative, only if you are not a cat …
Continue reading “The Role of a Faculty Community in Designing a Transformative Curriculum”
] The co-authors present key insights from their immersion in the Carnegie Study. Dr. Victoria Leonard is a Family Health Nurse Practitioner and is a noted researcher and consultant in family health care, infant and early childhood caregiving. At the time of the study, Dr. Leonard was teaching nursing at The University of San …